Owl Mountains on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
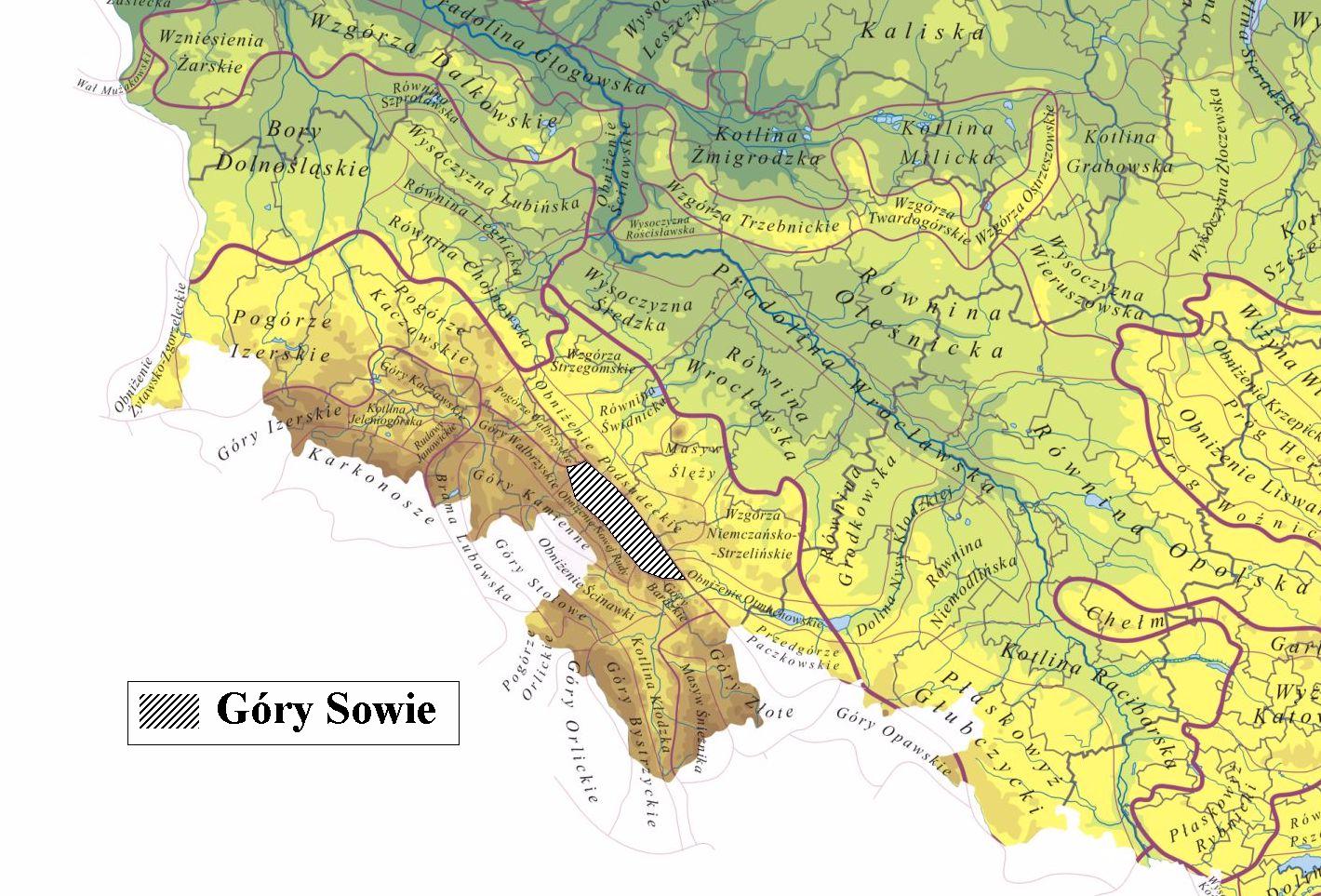 The Owl Mountains ( pl, Góry Sowie, cs, Soví hory, german: Eulengebirge) are a
The Owl Mountains ( pl, Góry Sowie, cs, Soví hory, german: Eulengebirge) are a
 The Owl Mountains cover an area of about and stretch over between the historic
The Owl Mountains cover an area of about and stretch over between the historic  The Precambrian
The Precambrian
 In
In
 The Owl Mountains ( pl, Góry Sowie, cs, Soví hory, german: Eulengebirge) are a
The Owl Mountains ( pl, Góry Sowie, cs, Soví hory, german: Eulengebirge) are a mountain range
A mountain range or hill range is a series of mountains or hills arranged in a line and connected by high ground. A mountain system or mountain belt is a group of mountain ranges with similarity in form, structure, and alignment that have ari ...
of the Central
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known a ...
Sudetes
The Sudetes ( ; pl, Sudety; german: Sudeten; cs, Krkonošsko-jesenická subprovincie), commonly known as the Sudeten Mountains, is a geomorphological subprovince in Central Europe, shared by Germany, Poland and the Czech Republic. They consi ...
in southwestern Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
. It includes a protected area
Protected areas or conservation areas are locations which receive protection because of their recognized natural, ecological or cultural values. There are several kinds of protected areas, which vary by level of protection depending on the ena ...
called Owl Mountains Landscape Park.
Geography
 The Owl Mountains cover an area of about and stretch over between the historic
The Owl Mountains cover an area of about and stretch over between the historic Lower Silesia
Lower Silesia ( pl, Dolny Śląsk; cz, Dolní Slezsko; german: Niederschlesien; szl, Dolny Ślōnsk; hsb, Delnja Šleska; dsb, Dolna Šlazyńska; Silesian German: ''Niederschläsing''; la, Silesia Inferior) is the northwestern part of the ...
n region and Kłodzko Land
Kłodzko Land ( pl, Ziemia kłodzka; cs, Kladsko; german: Glatzer Land) is a historical region in southwestern Poland.
The subject of Czech-Polish rivalry in the High Middle Ages, it became a Bohemian domain since the 12th century, although with ...
. Apart from the main ridge, the subdivisions of ''Garb Dzikowca'' and ''Wzgórza Wyrębińskie'' can be distinguished.
The range is bounded by the valley of the Bystrzyca river in the northwest, forming a natural border with the adjacent Waldenburg Mountains
The Wałbrzyskie Mountains or Waldenburg Mountains ( pl, Góry Wałbrzyskie; german: Waldenburger Bergland), sometimes called the Wałbrzyskie Highlands or Waldenburg Highlands, is one of the three mountain ranges that form the western part of the ...
(''Góry Wałbrzyskie''). In the southeast, the border is marked out by Srebrna Góra pass, separating them from the Bardzkie Mountains (''Góry Bardzkie''). In the north, the border is on Kotlina Distrabiekenstein and in the south on Obniżenie Noworudzkie and Włodzickie Hills. In the southwest, the broad Kłodzko Valley stretches to the Table Mountains (''Góry Stołowe''), the Stone Mountains (''Góry Kamienne''), and the border with the Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The ...
.
Seen from the Silesian Lowlands
Silesian Lowlands (or Silesian Plains, pl, Nizina Śląska, cs, Slezská nížina, german: Schlesische Niederung) are lowlands located in Silesia, Poland in Central Europe. A small part is located in the Czech Republic. It is part of the Centra ...
in the northeast, the Owl Mountains form a comparatively steep edge of the Central Sudetes, though the range is very diversified in terms of height. The highest peaks are Wielka Sowa
Wielka Sowa ("Great Owl", german: Hohe Eule) with a height of is the highest peak of the Owl Mountains, a range of the Central Sudetes. The mountain is located in Dzierżoniów County, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, in south-western Poland.
Geograph ...
("Great Owl", at in altitude) and Kalenica () with their observation tower
An observation tower is a structure used to view events from a long distance and to create a full 360 degree range of vision to conduct long distance observations. Observation towers are usually at least tall and are made from stone, iron, an ...
s. Other peaks reach heights from about to metres above sea level.
 The Precambrian
The Precambrian gneiss
Gneiss ( ) is a common and widely distributed type of metamorphic rock. It is formed by high-temperature and high-pressure metamorphic processes acting on formations composed of igneous or sedimentary rocks. Gneiss forms at higher temperatures a ...
rocks of the Owl Mountains constitute the oldest part of the Sudetes and are among the oldest in Europe. Other deposits include migmatite rocks, to a lesser extent also amphibolite
Amphibolite () is a metamorphic rock that contains amphibole, especially hornblende and actinolite, as well as plagioclase feldspar, but with little or no quartz. It is typically dark-colored and dense, with a weakly foliated or schistose (flak ...
, serpentinite
Serpentinite is a rock composed predominantly of one or more serpentine group minerals, the name originating from the similarity of the texture of the rock to that of the skin of a snake. Serpentinite has been called ''serpentine'' or ''s ...
, granulite, and pegmatite
A pegmatite is an igneous rock showing a very coarse texture, with large interlocking crystals usually greater in size than and sometimes greater than . Most pegmatites are composed of quartz, feldspar, and mica, having a similar silici ...
. Except for the summit clearings and the mountain passes, the Owl Mountains represent the spruce-clad type of mountains. There may be also observed a rare natural occurrence of beech
Beech (''Fagus'') is a genus of deciduous trees in the family Fagaceae, native to temperate Europe, Asia, and North America. Recent classifications recognize 10 to 13 species in two distinct subgenera, ''Engleriana'' and ''Fagus''. The ''Engl ...
es and European yew.
Project Riese
 In
In World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, a vast tunnel system was driven into the mountains near the village of '' Wüstewaltersdorf'' (present-day Walim) at the behest of the Nazi German
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
government. Presumably meant to serve as a Führer Headquarters replacing Wolf's Lair
The ''Wolf's Lair'' (german: Wolfsschanze; pl, Wilczy Szaniec) served as Adolf Hitler's first Eastern Front military headquarters in World War II.
The headquarters was located in the Masurian woods, near the small village of Görlitz in Ost ...
in East Prussia, the adit
An adit (from Latin ''aditus'', entrance) is an entrance to an underground mine which is horizontal or nearly horizontal, by which the mine can be entered, drained of water, ventilated, and minerals extracted at the lowest convenient level. Adit ...
s are linked to another tunnel complex beneath Książ Castle
Książ Castle ( pl, Zamek Książ, ; german: Schloss Fürstenstein) is a castle in northern Wałbrzych in Lower Silesian Voivodeship, Poland. The largest castle in the region of Silesia, it is the third-largest in Poland behind Malbork Castle an ...
(''Schloss Fürstenstein''), about in the northwest, built according to plans by Hermann Giesler
Hermann Giesler (2 April 1898, Siegen – 20 January 1987, Düsseldorf) was a German architect during the Nazi era, one of the two architects most favoured and rewarded by Adolf Hitler (the other being Albert Speer).
Early life and World Wa ...
. Parts of the extended complex are accessible and can be visited as part of a guided tour.
Tourism
Located about south of the regional capitalWrocław
Wrocław (; german: Breslau, or . ; Silesian German: ''Brassel'') is a city in southwestern Poland and the largest city in the historical region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the River Oder in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Europe, r ...
, the picturesque Owl Mountains are a popular destination for hikers
Hiking is a long, vigorous walk, usually on trails or footpaths in the countryside. Walking for pleasure developed in Europe during the eighteenth century.AMATO, JOSEPH A. "Mind over Foot: Romantic Walking and Rambling." In ''On Foot: A Histo ...
and day-trippers. At the foot of the range are well-known tourist places, like: Rzeczka
Rzeczka is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Walim, within Wałbrzych County, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, in south-western Poland.
It lies approximately south-west of Walim, south-east of Wałbrzych, and south-west of the reg ...
, Walim at the Wielka Sowa massif, Sokolec, Jugów, Sierpnica, and Zagórze Śląskie.
The mountains are covered by a network of tourist trails, including the "red trail", leading through most of Europe. Other destinations include: the Stone Tower on Wielka Sowa and the viewing tower on Kalenica, Fort Srebrna Góra
Fort Srebrna Góra or Srebrnogórska Fortress (german: Festung Silberberg, lit. Silver Mountain Fort) is a former military fort, now a monument and a museum, located in the town of Srebrna Góra (lit. Silver Mountain), Lower Silesian Voivodeship, ...
, Grodno Castle in Zagórze Śląskie, the adit complexes of Project Riese near Walim and the Mining Museum in Poland. Major towns at the foot of the Owl Mountains include Bielawa
Bielawa (german: Langenbielau; szl, Bielawa) is a town in southwestern Poland. Since 1999, it has been situated in Dzierżoniów County, Lower Silesian Voivodeship. From 1975 to 1998, it was part of the Wałbrzych Voivodeship. As of December 20 ...
, Dzierżoniów, Głuszyca, Jedlina-Zdrój, Nowa Ruda, Pieszyce, and Srebrna Góra.
See also
* Eulengebirgsbahn {{Authority control Sudetes Mountain ranges of Poland